Intelligent Automation
The Future of Operational Efficiency
The Catalyst for Operational Excellence
Introduction to Intelligent Automation - Intelligent Automation (IA) marks a significant milestone in the evolution of business processes automation, blending Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with the creativity of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This innovative technology enhances process automations with the ability to make decisions and learn from outcomes, ushering in a new era of efficiency. In the fiercely competitive landscape of today's market, IA has become a crucial element for companies aiming to optimize their operations and amplify productivity across all divisions. Distinguishing itself from traditional RPA, IA incorporates AI elements such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, enabling machines to tackle complex tasks, learn from data, and automate decision-making processes.
In today's competitive market, Intelligent Automation has emerged as an indispensable asset for top-tier companies seeking to streamline operations and elevate productivity across various business units. Automation extends beyond the routine task execution. The result is a significant enhancement in speed, accuracy, and flexibility of business processes, driving operational excellence and innovation. With its capability to transform data into actionable insights, Intelligent Automation is revolutionizing industries by providing solutions that adapt to evolving business needs.
What Is RPA?
Robotic Process Automation is software robots running on a physical or virtual machine in the Cloud. RPA is a form of business process automation that allows anyone to define a set of instructions for a robot or ‘bot’ to perform. RPA bots are capable of mimicking most human-computer interactions to carry out a ton of error-free tasks, at high volume and speed.
RPA is ultimately about automating some of the most mundane and repetitive computer-based tasks and processes in the workplace. Think copy-paste tasks and moving files from one location to another, for example. RPA automates everyday processes that once required human action – often a great deal of it performed in rote, time-consuming fashion. That’s also how RPA promises to boost efficiency for organizations.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) serves as the backbone of IA by automating routine, mundane tasks. RPA technology allows for the creation of software robots that can mimic human interactions with digital systems, performing high-volume, repetitive tasks without errors. From simple copy-paste actions to moving files and processing transactions, RPA lays the groundwork for efficiency improvements by automating tasks that traditionally consumed substantial human effort.
Assessing Automation Feasibility
Embarking on the journey of intelligent automation begins with a thorough assessment of processes to identify those best suited for IA. Essential criteria include the volume of work, the stability of the process, the complexity of decision points, and the structure of the data involved. This initial analysis helps pinpoint processes where IA can significantly impact efficiency and effectiveness. For instance, case studies show businesses harnessing IA to automate customer service inquiries, significantly reducing response times and increasing customer satisfaction.
It's not just about reducing the workload but about enriching the quality of work by eliminating errors and freeing up human capital to focus on strategic initiatives. As organizations embrace this smart technology, they witness substantial gains in customer satisfaction, a reduction in operational costs, and a robust boost in overall business performance. For businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve, Intelligent Automation is not just a tool but a strategic imperative. It's the key to unlocking potential, fostering growth, and ensuring sustainability in an increasingly digitized world. As Intelligent Automation continues to advance, it will further cement its role as a cornerstone of business operations, propelling companies towards unprecedented levels of success.
Successful Intelligent Automation initiatives start with a shared vision, a willingness for cross-team collaboration and the freedom to work through trial and error. The foundation of implementing successful business process automation lies in choosing the correct processes to automate and selecting the right tools to achieve the desired outcome. Before embarking on deploying intelligent automation solutions, it is important to first think through organizational challenges and internal resistance. By sharing and communicating the potential benefits of Intelligent automation, this should help build momentum for the intelligent automation project.
Gain organization buy-in
Scaling Intelligent Automation Initiatives
For organizations aiming to expand their intelligent automation capabilities, establishing a Center of Excellence (CoE) is a strategic move. This dedicated team oversees the IA lifecycle, from pilot projects to full-scale implementation, ensuring alignment with business objectives and facilitating knowledge sharing. By adopting an Agile methodology, the CoE promotes adaptability and rapid progress, laying a foundation for sustained automation success. Whether reducing operational costs, enhancing customer experiences, or driving innovation, Intelligent Automation is pivotal for businesses prepared to embrace the digital age.
Key Questions for identifying Intelligent Automation Processes:
Is there a sufficient volume of work that will justify the cost? Processes might be a fit for intelligent automation but with low volume, may not have a sufficient impact to justify the upfront and ongoing investment.
Will there be changes to the process in the short term? Processes with anticipating changes in the short term delayed to prevent rework.
How many decision points are required? Sophisticated processes with multiple decision points will require a more complex solution.
Is the data structured? Picking processes with (mostly) structured data offers quicker wins with less complexity for Intelligent Automation.
Analyze and Evaluating Intelligent Automation
To do this, process analysts should:
Collect current-state system architecture
Identify all available tools and documentation for each process
Determine data sources, highlighting structured vs. unstructured
Count the number of decision points that might be needed
Calculate aggregated potential time savings available
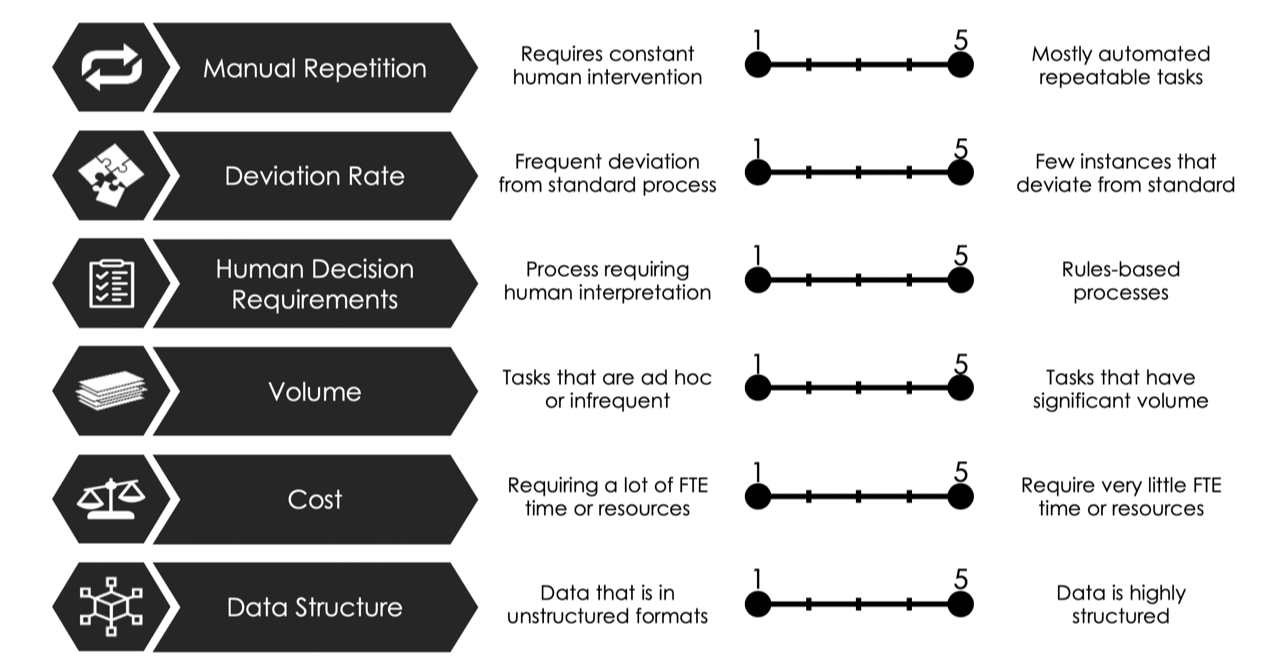
Once the team eliminates poorly fit processes from the automation initiative, the remaining options should be scored against a set of characteristics inherent to each process.
The output of this assessment is the feasibility score, representing how easily automation solutions would be to implement for each process, and is the first major factor in the final prioritization.
Process automation professionals have varying opinions about characteristics affecting automation feasibility, but the following are sure to provide a balanced and thorough assessment of each process.
Prioritizing Automations
There are many factors to consider, and business leaders should align with what their desired outcome would look like and prioritize accordingly. These potential benefits should be ranked and assigned a relative weighting against key business drivers. This will provide a tailored impact score that aligns with the goals of each organization and assists in comparing potential ROI from various initiatives. The ROI calculation should try to include all qualitative and quantitative benefits. Initially at a high level, however once the top processes are selected, a deeper analysis should be completed.
Once the ROI is calculated across each process can be ranked and plotted on a prioritization matrix. This makes it easy to identify quick wins and which processes will require a more significant investment to automate. Upon completing of the prioritization model, a detailed business case can be built to secure buy-in from senior leadership to pursue the automation journey. Multiple solutions should be compared when determining best fit and alignment with specific use cases.